| https://link.springer.com/journal/42241/32/4 |
CONTENTS
REVIEW ARTICLE
SPECIAL COLUMN ON THE 2020 SPHERIC Harbin International Workshop (GUEST EDITORS A-MAN ZHANG, SHI-PING WANG, PENG-NAN SUN)
ARTICLES
LETTERS
Editorial Message
| https://link.springer.com/journal/42241/32/4 |
由于北极海冰的覆盖面积和厚度持续缩减,极地航行和资源开发日益现实,巨大的经济利益和重要的发展意义促使国际市场对极地装备的需求越来越迫切。极地装备运行于冰水耦合环境中,冰-水-结构物的复杂耦合作用成为极地船舶和海洋工程结构物设计和运行的核心问题之一。作为一类特殊的流固耦合问题,冰-水-结构物耦合问题涉及多介质、多界面和多尺度,无论在理论分析还是数值模拟上都存在巨大挑战。近年来,在冰-水-结构物耦合作用方面的研究也成为了水动力学领域的一大热点问题。
On the development of ice-water-structure interaction(share this article: https://rdcu.be/b6mz4)论文由哈尔滨工程大学船舶工程学院倪宝玉教授、韩端锋教授等人撰写,该论文针对冰-水-结构物耦合作用这一热点问题,分别从理论解析(包含半解析-半数值)、数值模拟和实验研究等三个方面综述目前国内外在这一研究上的前沿进展。论文重点放在数值模拟的进展上,分别介绍了基于光滑粒子水动力学(SPH)、基于离散元-计算流体力学耦合法(DEM-CFD)、基于格子玻尔兹曼方法(LBM)、基于有限元法(FEM)和基于近场动力学(PD)等多种数值算法在冰-水-结构物耦合方面的研究和应用情况。论文重点综述了国内外在相关方法上研究比较活跃的团队的工作,并结合目前研究前沿预测了各种方法未来的发展趋势。论文旨在为相关研究提供一定的参考,尤其让初学者对于各种方法的优劣势有一定的了解。
论文也阐述了作者团队的部分研究工作进展,相关图片如下所示。
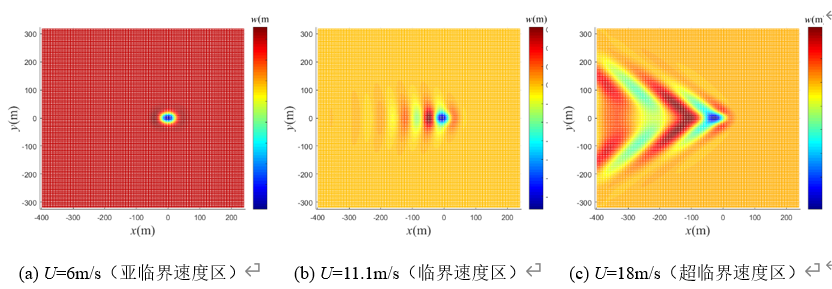
图1 冰面载荷不同移动速度下冰的变形情况
图2 不同冰况下船舶在碎冰中的航行
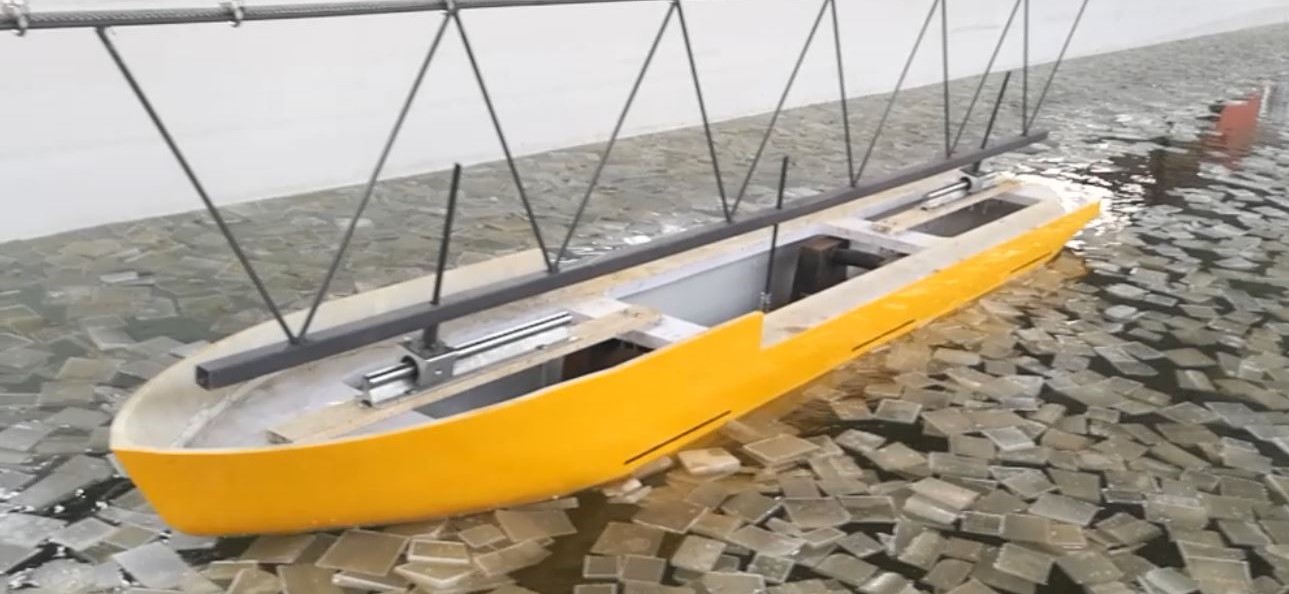 图3 船模在碎冰航道内航行
图3 船模在碎冰航道内航行
第一作者简介:
 倪宝玉,哈尔滨工程大学船舶工程学院教授,博导,英国伦敦大学学院(UCL)博士后。现为工信部“极地装备技术”重点实验室副主任,中国科协“青年人才托举工程”获得者,中国博士后国际交流计划入选者,《Journal of Hydrodynamics》、《Shock & Vibration》、《Journal of Marine Science and Application》、《水动力学研究与进展》编委,英国皇家造船工程学会(RINA)会员等。主要研究方向包括冰-水-结构物耦合特性、冰区船舶力学特性、高速砰击水动力学和气泡动力学等。国家自然科学基金面上/青年项目、军科委基础加强计划课题、国家重点研发计划课题等10余项项目负责人;国家自然科学基金重点项目、欧盟地平线2020计划项目、英国劳氏基金会项目等10余项技术负责人。申请发明专利20余项,软件著作权6项。在国内外学术期刊上发表论文40余篇,著有专著2部,荣获中国海洋工程科学技术奖二等奖等。
倪宝玉,哈尔滨工程大学船舶工程学院教授,博导,英国伦敦大学学院(UCL)博士后。现为工信部“极地装备技术”重点实验室副主任,中国科协“青年人才托举工程”获得者,中国博士后国际交流计划入选者,《Journal of Hydrodynamics》、《Shock & Vibration》、《Journal of Marine Science and Application》、《水动力学研究与进展》编委,英国皇家造船工程学会(RINA)会员等。主要研究方向包括冰-水-结构物耦合特性、冰区船舶力学特性、高速砰击水动力学和气泡动力学等。国家自然科学基金面上/青年项目、军科委基础加强计划课题、国家重点研发计划课题等10余项项目负责人;国家自然科学基金重点项目、欧盟地平线2020计划项目、英国劳氏基金会项目等10余项技术负责人。申请发明专利20余项,软件著作权6项。在国内外学术期刊上发表论文40余篇,著有专著2部,荣获中国海洋工程科学技术奖二等奖等。
通信作者简介:

韩端锋,哈尔滨工程大学船舶工程学院教授,博导。现为科技部中国-俄罗斯极地技术与装备“一带一路”联合实验室主任,国家重点研发计划海洋领域专家组成员,船舶与海洋工程专业教学指导委员会副主任,《哈尔滨工程大学学报》主任编委等。曾获全国优秀科技工作者、黑龙江省模范教师、黑龙江省教育系统先进工作者等称号。主要研究方向包括极地装备与技术、数字化造船技术、舰船操纵模拟仿真研究、载人潜水器关键技术等。主持国家自然科学基金重点项目、军科委基础加强计划、国家重点研发计划等项目50余项,成果应用于我国“雪龙2号”极地科考船、全球最新极地甲板运输船等多种船型。
| Top-Articles-of-JHD-in-2019-data-from-Springer-Nature.docx (706 downloads) |
| Title | Author | Article Type | Volume | Issue | Year* | Article Requests 2019 | |
| 1 | Spectral/hp element methods: Recent developments, applications, and perspectives | Hui Xu et al. | Review Paper | 30 | 1 | 2018 | 1,662 |
| 2 | Third generation of vortex identification methods: Omega and Liutex/Rortex based systems | Chaoqun Liu et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 2 | 2019 | 487 |
| 3 | Application of deep learning method to Reynolds stress models of channel flow based on reduced-order modeling of DNS data | Zhen Zhang et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 1 | 2019 | 278 |
| 4 | Bubble dynamics and its applications | Shi-Ping Wang et al. | Review Paper | 30 | 6 | 2018 | 220 |
| 5 | A review of cavitation in hydraulic machinery | Xian-wu Luo et al. | Review Paper | 28 | 3 | 2016 | 195 |
| 6 | Development of naoe-FOAM-SJTU solver based on OpenFOAM for marine hydrodynamics | Jian-hua Wang et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 1 | 2019 | 181 |
| 7 | A selected review of vortex identification methods with applications | Yu-ning Zhang et al. | Original Paper | 30 | 5 | 2018 | 149 |
| 8 | Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in fluid-structure interactions | A-man Zhang et al. | Review Paper | 29 | 2 | 2017 | 136 |
| 9 | The structure of turbulent flow through submerged flexible vegetation | Wen-xin Huai et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 2 | 2019 | 135 |
| 10 | SPH modeling of fluid-structure interaction | Luhui Han et al. | Original Paper | 30 | 1 | 2018 | 130 |
| Title | Author | Article Type | Volume | Issue | Year* | Article Requests 2019 | |
| 1 | Spectral/hp element methods: Recent developments, applications, and perspectives | Hui Xu et al. | Review Paper | 30 | 1 | 2018 | 1,662 |
| 2 | Third generation of vortex identification methods: Omega and Liutex/Rortex based systems | Chaoqun Liu et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 2 | 2019 | 487 |
| 3 | Application of deep learning method to Reynolds stress models of channel flow based on reduced-order modeling of DNS data | Zhen Zhang et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 1 | 2019 | 278 |
| 4 | Bubble dynamics and its applications | Shi-Ping Wang et al. | Review Paper | 30 | 6 | 2018 | 220 |
| 5 | Development of naoe-FOAM-SJTU solver based on OpenFOAM for marine hydrodynamics | Jian-hua Wang et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 1 | 2019 | 181 |
| 6 | A selected review of vortex identification methods with applications | Yu-ning Zhang et al. | Original Paper | 30 | 5 | 2018 | 149 |
| 7 | Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in fluid-structure interactions | A-man Zhang et al. | Review Paper | 29 | 2 | 2017 | 136 |
| 8 | The structure of turbulent flow through submerged flexible vegetation | Wen-xin Huai et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 2 | 2019 | 135 |
| 9 | Explicit formula for the Liutex vector and physical meaning of vorticity based on the Liutex-Shear decomposition | Yi-qian Wang et al. | Original Paper | 31 | 3 | 2019 | 130 |
| 10 | SPH modeling of fluid-structure interaction | Luhui Han et al. | Original Paper | 30 | 1 | 2018 | 130 |
| Title | Author | Publication Type | Publication Date | DOI | Volume | Issue | Total Citations* | Citations for IF 2018 |
| A review of cavitation in hydraulic machinery | Luo, Xian-wu; Ji, Bin; Tsujimoto, Yoshinobu | Review | 01-06-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60638-8 | 28 | 3 | 95 | 25 |
| Smoothed particle hydrodynamics and its applications in fluid-structure interactions | Zhang, A-man; Sun, Peng-nan; Ming, Fu-ren; Colagrossi, A. | Review | 01-04-2017 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60730-8 | 29 | 2 | 46 | 19 |
| Large eddy simulation of turbulent attached cavitating flow with special emphasis on large scale structures of the hydrofoil wake and turbulence-cavitation interactions | Ji, Bin; Long, Yun; Long, Xin-ping; Qian, Zhong-dong; Zhou, Jia-jian | Article | 01-02-2017 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60715-1 | 29 | 1 | 40 | 19 |
| Verification and validation of URANS simulations of the turbulent cavitating flow around the hydrofoil | Long, Yun; Long, Xin-ping; Ji, Bin; Huai, Wen-xin; Qian, Zhong-dong | Article | 01-08-2017 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60774-6 | 29 | 4 | 38 | 18 |
| On the modeling of viscous incompressible flows with smoothed particle hydrodynamics | Liu, Mou-Bin; Li, Shang-ming | Review | 01-10-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60676-5 | 28 | 5 | 40 | 16 |
| Mixed convection flow of jeffrey nanofluid with thermal radiation and double stratification | Abbasi, F. M.; Shehzad, S. A.; Hayat, T.; Alhuthali, M. S. | Article | 01-10-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60686-8 | 28 | 5 | 31 | 12 |
| Numerical simulation of hydraulic force on the impeller of reversible pump turbines in generating mode | Li, Jin-wei; Zhang, Yu-ning; Liu, Kai-hua; Xian, Hai-zhen; Yu, Ji-xing | Article | 01-08-2017 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60773-4 | 29 | 4 | 13 | 8 |
| Hull form optimization of a cargo ship for reduced drag | Huang, Fuxin; Yang, Chi | Article | 01-04-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60619-4 | 28 | 2 | 21 | 7 |
| Numerical investigation of unsteady cavitating turbulent flows around twisted hydrofoil from the Lagrangian viewpoint | Cheng, Huai-yu; Long, Xin-ping; Ji, Bin; Zhu, Ye; Zhou, Jia-jian | Article | 01-08-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60674-1 | 28 | 4 | 19 | 6 |
| Hydrodynamic modelling of flow impact on structures under extreme flow conditions | Liang, Qiuhua; Chen, Kai-cui; Hou, Jingming; Xiong, Yan; Wang, Gang; Qiang, Juan | Article | 01-04-2016 | 10.1016/S1001-6058(16)60628-5 | 28 | 2 | 11 | 6 |
How is the Altmetric score calculated? The score is a weighted count
The score is a weighted count of the different sources (newspaper stories, tweets, blog posts, comments) that mention the paper.
Why is it weighted? To reflect the relative importance of each type of source. It’s easy to imagine that the average newspaper story is more likely to bring attention to the paper than the average tweet. This is reflected in the default weightings.
| News | Blogs | Q&A forums | Google+ | |||||||
| 8 | 5 | 2.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | |||||
| Score | Article DOI | Title | Author(s) | Publication Date | ||||||
| 8 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(09)60249-3 | Dynamic pressures on curved front seawall models under random waves | K. V. ANAND, V. SUNDAR, S. A. SANNASIRAJ | 01-10-2010 | ||||||
| 4 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(16)60614-5 | A new biomimicry marine current turbine: Study of hydrodynamic performance and wake using software OpenFOAM | YUNG-JEH CHU | 01-02-2016 | ||||||
| 3 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(13)60365-0 | Influence of emergent macrophyte (Phragmites australis) density on water turbulence and erosion of organic-rich sediment | JUKKA HORPPILA, JONI KAITARANTA, LAURA JOENSUU, LEENA NURMINEN | 01-04-2013 | ||||||
| 3 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(16)60791-6 | Numerical simulation of three-dimensional breaking waves and its interaction with a vertical circular cylinder | ZHIHUA XIE, LIN LU, THORSTEN STOESSER, JIAN-GUO LIN, DIMITRIOS PAVLIDIS, PABLO SALINAS, CHRISTOPHER C. PAIN, OMAR K. MATAR | 01-10-2017 | ||||||
| 2 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(16)60705-9 | Effects of thermal boundary conditions on the joule heating of electrolyte in a microchannel | M. Y. ABDOLLAHZADEH JAMALABADI, J. H. PARK, M. M. RASHIDI, J. M. CHEN | 01-10-2016 | ||||||
| 1 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(16)60699-6 | New prospects for computational hydraulics by leveraging high-performance heterogeneous computing techniques | QIUHUA LIANG, LUKE SMITH, XILIN XIA | 01-12-2016 | ||||||
| 1 | 10.1016/s1001-6058(16)60628-5 | Hydrodynamic modelling of flow impact on structures under extreme flow conditions | QIUHUA LIANG, KAI-CUI CHEN, JINGMING HOU, YAN XIONG, GANG WANG, JUAN QIANG | 01-04-2016 | ||||||
2020年5月,广东虎门大桥发生的流致振动(Flow-induced Vibration, FIV)事件使大众对FIV的关注度急剧上升,也让人马上联想起震惊世界的1940年塔科马大桥的垮塌事件(图1)。众所周知,钝体绕流会产生卡门涡街,其泄涡频率与结构固有频率接近时容易产生涡激振动(VIV)。这可能诱发结构的疲劳破坏,导致结构的安全事故。为了减弱甚至消除这种VIV,在海洋工程领域,人们发明了各种抑制装置,在实际工程中有着广泛应用。近10来年的研究发现,在圆柱结构附加整流罩或分离盘这样的附加结构在一些条件下有很好的VIV抑制作用;然而,在另一些条件下,可能发生比VIV振幅更大,类似于土木桥梁领域方柱结构的驰振(Galloping)现象,这种驰振反而加强振动,加剧破坏。需要我们深入思考和研究这些抑制装置的作用机理,探讨新的FIV抑制装置。
本期栏目中,我们推荐上海交通大学王嘉松教授团队与麻省理工学院机械工程范迪夏博士,在Journal of Hydrodynamics第32卷第3期(2020)发表的关于“海洋工程中圆柱体的流致振动问题”综述文章 A review on flow-induced vibration of offshore circular cylinders(share this artilce: https://rdcu.be/b5u8I)。
图1 (来源于网络)虎门大桥(2020)和塔科马大桥(1940)的流致振动
该文以“单柱体VIV→复杂多柱体WIV→工程抑制与驰振”为主线,由简单到复杂,由抽象模型到实际应用,由实验室和数值研究到工业界实践,翔实地梳理阐述了10多年来学界与业界在海洋工程中圆柱体的FIV问题研究上的进展。
(1)单柱体VIV:强调流固耦合问题的复杂度
FIV中广泛存在着流固耦合(FSI)现象,即结构在流体载荷下发生变形或运动,同时结构又对流场分布产生影响,流固二者相互作用相互影响。FIV的FSI机理还没有被完全阐明,其背后存在着的如附加质量、高阶流体力等问题仍有待进一步研究。FSI的高度复杂性为实验和数值研究提出了诸多挑战。
从刚性结构到柔性结构,从强迫振动到自由振动,FSI的复杂程度逐渐加深。文章对基于三种基本模型的单柱VIV研究做了归纳:(1)受弹性支撑的刚性圆柱;(2)做强迫振动的刚性圆柱;(3)做自由振动的柔性圆柱(图2)。揭示了在均匀来流作用下的刚性圆柱以及柔性圆柱的复杂表现和内在机理,建立了三种基本模型之间的联系。
图2 柔性单管自由振动(左-模型尺度,右-实尺度)
(2)多柱体WIV:总结多柱体结构的流动干涉及流固耦合响应干涉特征
在海洋工程中,许多FIV问题涉及到由两个或两个以上圆柱体组成的柱群或者管丛结构,比如用于海上钻井和生产平台的立管阵列。当流体流经这些近距布置的多管柱体结构时,结构的尾流之间会发生流动干涉形成复杂尾涡形态。若结构可发生变形或位移响应时,尾流与结构间发生再耦合也会导致引起与单圆柱体VIV响应截然不同的结构响应(图3)。
文章从三个方面对柱群FIV干涉的研究作了总结:(1)固定圆柱体的流动干涉形态;(2)上游尾流与下游结构再耦合响应-WIV;(3)典型布置方式下多管柱结构FIV干涉响应特征。
图3 双管FIV干涉(左-模型尺度梯度流,右-实尺度均匀流)
(3)VIV抑制与驰振: 指出传统的抑制措施可能引起galloping,一种更不利的振动
在FIV的作用下,细长海洋结构物发生周期性振动,这会导致静载的增加和严重的疲劳破坏,通过在柱体上适当地附属抑振装置可以抑制这种振动。文章首次收集国内外数据对三种最常用的抑振装置:螺旋列板(helical strake)、整流罩(fairing)和分离盘(splitter plate)的抑制效果做了归纳(图4),表明各有优缺点,有的振幅抑制佳,却加大了曳力;有的曳力和振幅都小,但有时可能导致新的负面影响。尽管附属抑振装置的方法在大量工程领域得到了有效应用,但是研究发现,在某些情况下附属抑振装置可能会导致驰振,反而增大振幅。无论是与固有频率的关系,还是振动幅值的大小,这种驰振与传统的VIV有着本质的不同,它可能是锁頻(空气中),也可能低频(水中),可能是自激的(大约化速度启动),也可能是他激的(与VIV耦合),等等,这些机制有待我们深入研究。从另一角度来看,涡激振动或驰振还可通过能量转化加以获取及利用。
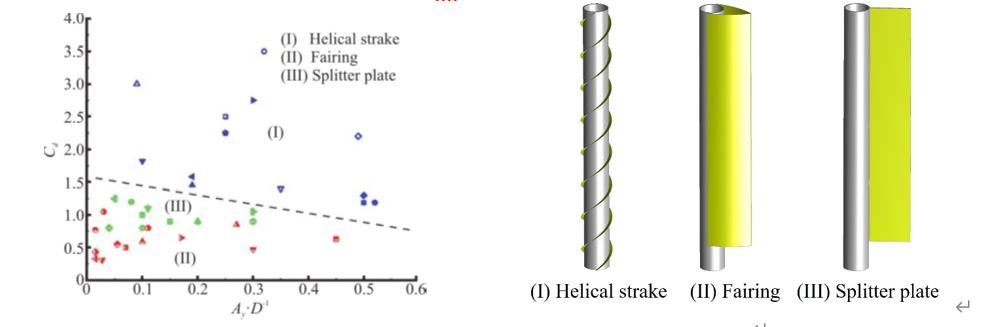 图4 常见VIV抑制装置的效果
图4 常见VIV抑制装置的效果
(4)文章在最后给出了5点研究展望,表明挑战与机遇并存:
作者简介:
 王嘉松 上海交通大学船建学院长聘教授,博士生导师,上海市闵行区领军人才。主要从事高精度数值计算方法及其应用,涡激振动机理及其抑制,流致振动及驰振,流固耦合,风洞与水槽实验,大气环境动力学等方向的研究,近来也从事流致振动能量获取的研究。作为负责人获上海科技进步一等奖,主要参与者获得中国石油化工联合会科技进步一等奖。担任《Journal of Hydrodynamics》和《水动力学研究与进展》编委。
王嘉松 上海交通大学船建学院长聘教授,博士生导师,上海市闵行区领军人才。主要从事高精度数值计算方法及其应用,涡激振动机理及其抑制,流致振动及驰振,流固耦合,风洞与水槽实验,大气环境动力学等方向的研究,近来也从事流致振动能量获取的研究。作为负责人获上海科技进步一等奖,主要参与者获得中国石油化工联合会科技进步一等奖。担任《Journal of Hydrodynamics》和《水动力学研究与进展》编委。
 范迪夏 加拿大皇后大学机械与材料工程助理教授,他在2019年获得麻省理工学院机械学院的博士学位,2019-2020任麻省理工学院助理研究员。其主要的研究兴趣为流固耦合,漩涡流体的控制与感知以及仿生流体在船舶操纵上的应用。
范迪夏 加拿大皇后大学机械与材料工程助理教授,他在2019年获得麻省理工学院机械学院的博士学位,2019-2020任麻省理工学院助理研究员。其主要的研究兴趣为流固耦合,漩涡流体的控制与感知以及仿生流体在船舶操纵上的应用。
空化和多相流是流体力学的一个重要课题,也是实现装备系统稳定性、安全可靠性的重要问题。为加强交流以共同促进空泡、空化及相关多相流动的研究,2019年4月19日至4月22日,在上海召开了第三届空化和多相流国际会议(The 3rd International Symposium of Cavitation and Multiphase Flow, ISCM2019)。旨在为国内外专家及青年学者搭建合作平台,交流空化和多相流领域的最新研究成果及其应用,共同探索学术难题。同时,促进水动力学与重大工程/重要装备的相互融合与提高。
本次会议由上海大学、《水动力学研究与进展》编委会联合主办,北京国际力学中心、喷水推进技术重点实验室等多家单位协办单位。 来自意大利国家研究委员会罗马海洋工程研究所、日本东北大学和早稻田大学、荷兰特温特大学、西班牙加泰罗尼亚大学、斯洛文尼亚卢布尔雅那大学以及清华大学等国内高校研究所,近200名专家学者出席了此次研讨会。
美国工程院院士、加利福尼亚大学Said Elghobashi教授、英国伦敦帝国理工大学Yannis Hardalupas教授、新加坡国立大学Khoo Boo Cheong教授、德国马格德堡大学Claus-Dieter Ohl教授、法国国家科学研究中心Pierre-Yves Lagrée教授、瑞典Chalmers 理工大学Rickard Bensow教授、美国密歇根大学的Steven Ceccio教授、中国船舶科学研究中心的彭晓星研究员以及浙江大学林建忠教授等国内外知名学者,给参会者做了精彩的特邀报告。此外,为期三天的研讨会上,还设置了多场专题讨论,涉及水力机械内部空化多相流、空化及多相流数值计算与实验、空化多相流冲蚀及防冲蚀技术、空化与多相流诱导的流固耦合、空化流和多相流的多尺度模拟、空化产生的冲击波和微射流、气泡和汽泡的非线性振荡等,使得学者们在浓郁的气氛中得以充分的交流和研讨。本次大会形式多样、内容丰富、讨论气氛活跃。
 会议从大会邀请报告中选取了三篇论文在Journal of Hydrodynamics上作为专栏进行了发表(https://link.springer.com/journal/42241/32/1),
会议从大会邀请报告中选取了三篇论文在Journal of Hydrodynamics上作为专栏进行了发表(https://link.springer.com/journal/42241/32/1),
第一篇由美国密歇根大学的Steven Ceccio教授提供,《Effect of Compressibility on Bubbly Cavitating Flows 》(share this artilce: https://rdcu.be/b5u8I)介绍了泡状空化流动中的压缩性效应。该文指出泡状空化流动中存在大量的气泡使得本地声速较低,易形成超声速流动。作者在不同的几何形状的绕流问题中均发现了泡状激波(bubbly shocks),并指出泡状激波是空化流动失稳的重要原因。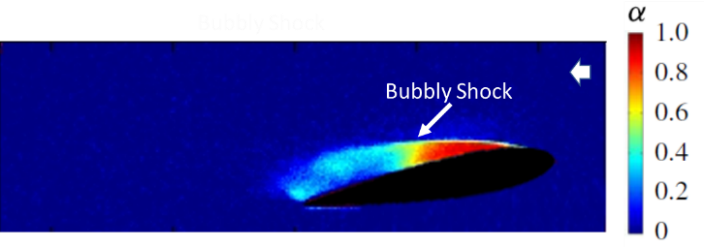 第二篇由瑞典Chalmers University of Technology的Rickard E Bensow教授提供,《Hydrodynamic mechanisms of aggressive collapse events in leading edge cavitation 》(share this artilce:https://rdcu.be/b5u8N )介绍了Naca0009水翼前缘局部空化结构溃灭的实验与数值模拟研究。通过比较发现可压缩求解器可以较好的获取瞬态空化流动结构中的溃灭现象,在此基础上利用计算了空化结构溃灭形成的侵蚀力,计算结果与油膜法空蚀实验获取的图案有很强的相关性,并发现了四个空蚀风险高的区域。
第二篇由瑞典Chalmers University of Technology的Rickard E Bensow教授提供,《Hydrodynamic mechanisms of aggressive collapse events in leading edge cavitation 》(share this artilce:https://rdcu.be/b5u8N )介绍了Naca0009水翼前缘局部空化结构溃灭的实验与数值模拟研究。通过比较发现可压缩求解器可以较好的获取瞬态空化流动结构中的溃灭现象,在此基础上利用计算了空化结构溃灭形成的侵蚀力,计算结果与油膜法空蚀实验获取的图案有很强的相关性,并发现了四个空蚀风险高的区域。 第三篇由新加坡国立大学的Khoo Boo Cheong教授提供,《Numerical Investigation on Free Surface Effect on the Supercavitating Flow over a Low Aspect Ratio Wedge-Shaped Hydrofoil》(share this artilce:https://rdcu.be/b5u8T) 介绍了近自由液面处超空泡流动的数值模拟研究。分析了浸没深度及水翼的长宽比对自由液面及超空泡形态的影响,同时获取了不同的流动图案及涡结构。
第三篇由新加坡国立大学的Khoo Boo Cheong教授提供,《Numerical Investigation on Free Surface Effect on the Supercavitating Flow over a Low Aspect Ratio Wedge-Shaped Hydrofoil》(share this artilce:https://rdcu.be/b5u8T) 介绍了近自由液面处超空泡流动的数值模拟研究。分析了浸没深度及水翼的长宽比对自由液面及超空泡形态的影响,同时获取了不同的流动图案及涡结构。
此外,本期中还另收录了两篇空化流动相关的快报,一篇由武汉大学的季斌博士提供,《Spatial and spectral investigation of turbulent kinetic energy in cavitating flow generated by Clark-Y hydrofoil》(share this artilce:htt://rdcu.be/b5u8W) 介绍了Clark-Y hydrofoil空化流动中湍流动能的时空分布特性,以及湍动能的频谱特征。另一篇由中国船舶与海洋设计研究院张伟博士提供,《Numerical simulation of condensation shock in partial cavitating flow on a hydrofoil》介绍了非稳态空化流动中凝聚激波的数值计算研究,提出了采用不可压缩求解器获取凝聚激波的方法,并显示了三维的空化流动结构。
客座编辑介绍:
张伟,中国船舶与海洋设计研究院,喷水推进技术重点实验室,高级工程师。主要从事流体力学、湍流与空化流动,以及人工智能及机器学习在流体学中的应用研究。担任Journal of hydrodynamics编委。